Perforating branches supply the posterior limb of the internal capsule part of the head and body of the caudate and globus. The Middle Cerebral Artery MCA is the most common site of stroke.

Identify The Vessel Recognize The Stroke American Nurse
The middle cerebral artery MCA is the largest of the three major arteries that channels fresh blood to the brain.
. And the temporal branches of the middle cerebral. The anterior cerebral arteries supply the anteromedial portion of the cerebrum. Conceptually as depicted in this diagram the circle of Willis is the centre of the cerebral circulation and from it blood flows into the anterior.
Supplies most of the temporal lobe anterolateral frontal lobe and parietal lobe. MCA infarcts occur in two general regions. The MCA is part of the circle of Willis anastomotic system within the brain which forms when the anterior cerebral arteries anastomose anteriorly with each other through the anterior communicating artery and posteriorly with the two posterior.
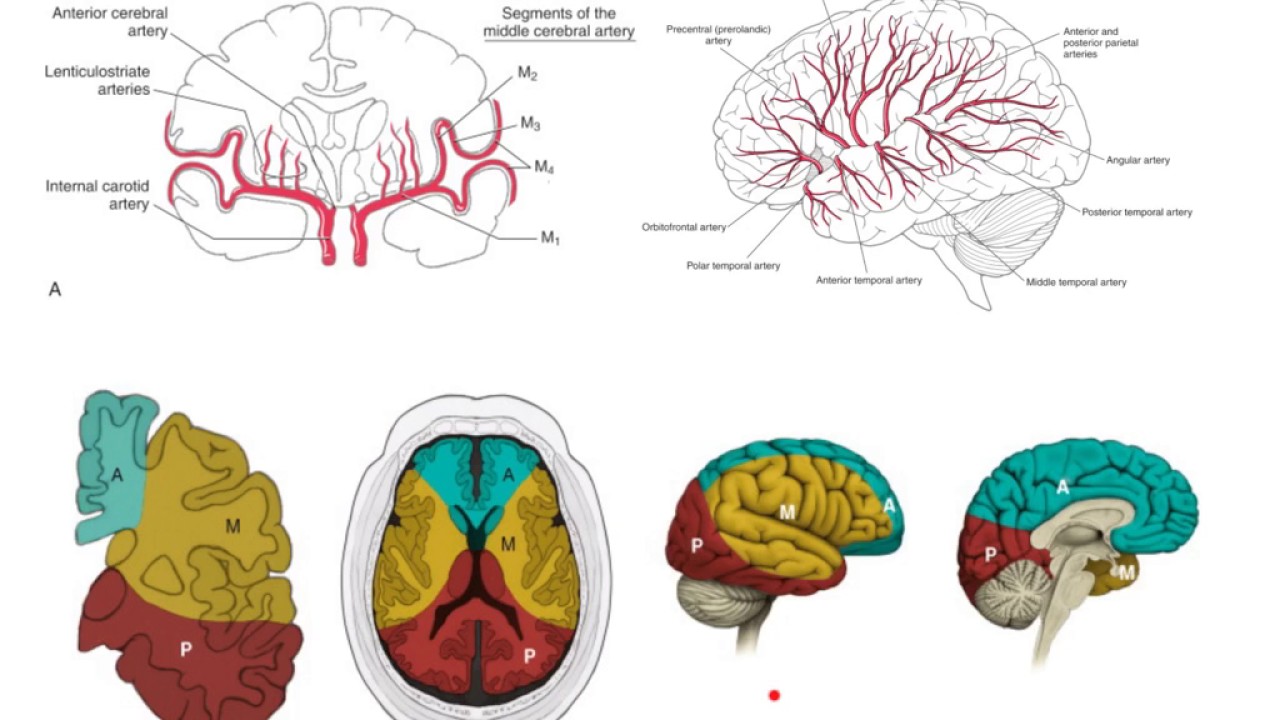
MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY FIGURE 1 The first large branch of the middle cerebral artery MCA is a large arterial trunk which supplies the entire temporal lobe by forming the temporopolar artery TPA anterior temporal artery ATA middle temporal artery MTA and posterior temporal artery PTA. The superior upper or suprasylvian MCA branch gives rise to several arteries that supply much of the lateral and inferior frontal lobe and the anterior lateral parts of the parietal lobe. The posterior cerebral arteries supply both the medial and lateral parts.
Movement of right head neck trunk and arm. It branches directly from the internal carotid artery and consists of four main branches M1 M2 M3 and M4. The middle carotid artery supplies parts of the brain responsible for movement and feeling in the trunk limbs and face.
3 rows The middle cerebral artery MCA is a terminal branch of the internal carotid artery and is part. These vessels provide blood supply to parts of the frontal temporal and parietal lobes of the brain as well as deeper structures including the caudate internal capsule. The parietal branches supply the postcentral gyrus inferior parietal lobule and lower part of the superior parietal lobule.
Clinical Significance edit edit source The middle cerebral artery is the most common pathologically affected blood vessel overall. It branches directly from the internal carotid artery and consists of four main branches M1 M2 M3 and M4. It supplies the greater part of the lateral cerebral surface including the main motor and sensory areas as well as giving the striate arteries which supply deep structures including the internal capsule.
The middle cerebral artery MCA is the most common artery involved in acute stroke. The middle cerebral artery is the largest branch of the internal carotid. The MCA passes laterally just underneath the frontal lobe ultimately taking up a position between the temporal and frontal lobes in the Sylvian fissure.
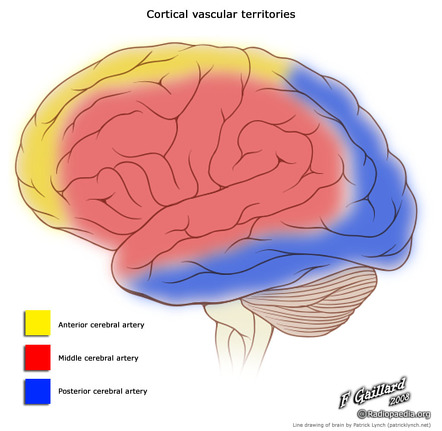
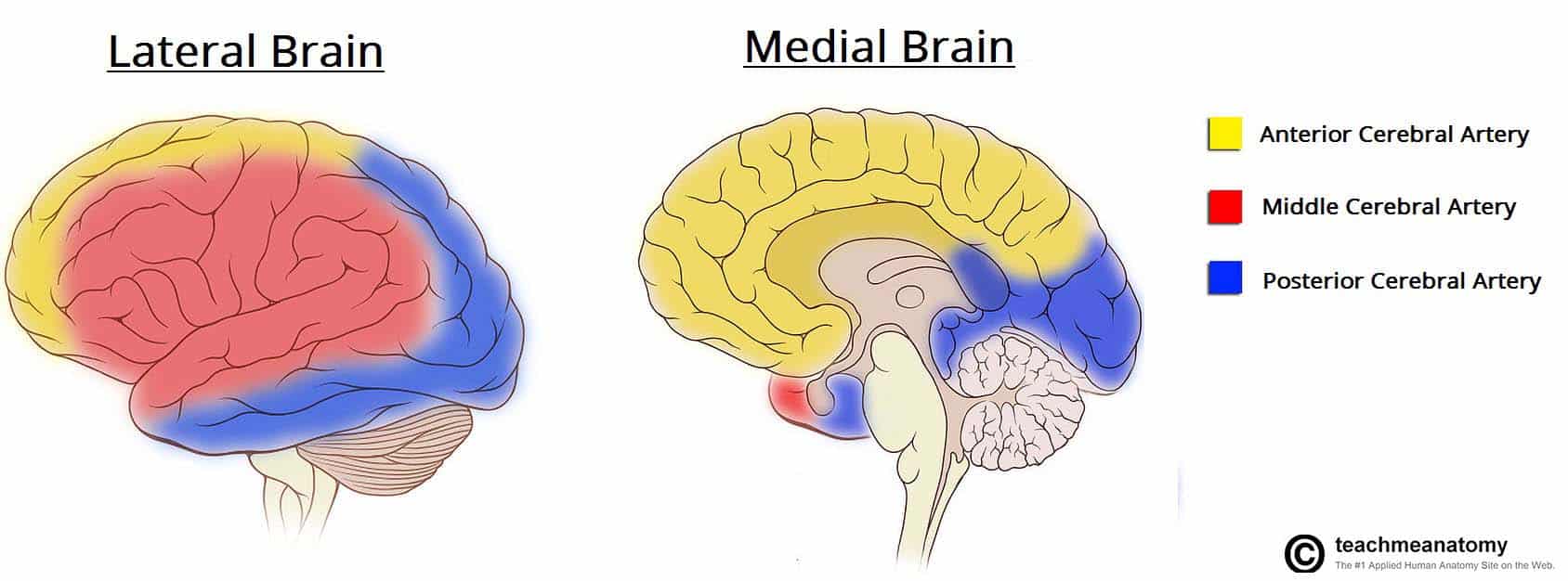
Anterior middle and posterior. Superficial divisions and lenticulostriate branches. They each supply a different portion of the cerebrum.
In addition they supply part of the internal capsule and basal ganglia. This artery also supplies blood to the primary sensory and motor areas of the face hand throat and arm2. These vessels provide blood supply to parts of the frontal temporal and parietal lobes of the brain as.
The middle cerebral arteries are situated laterally supplying the majority of the lateral part of the brain. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.
There are three cerebral arteries. The middle cerebral artery is the vessel that feeds into the COW by providing the anterior communicating artery and the posterior cerebral artery connects via the posterior communicating artery. Anatomically the MCA is divided into two segments M1 and M23.
Left Superficial Division Right Superficial Division Lenticulostriate Branches Perfusion Areas Clinical Syndromes MCA Supply 3D MOTOR CORTEX. The middle cerebral artery MCA is the most common artery involved in acute stroke. The initial part of the MCA is a single vessel called the stem or M1 segment.
The artery supplies a portion of the frontal lobe and the lateral surface of the temporal and parietal lobes including the primary motor and sensory areas of the face throat hand and arm and in the dominant hemisphere the areas for speech. The middle cerebral artery MCA has a large diameter and branches at an acute angle from the internal carotid. The middle cerebral artery MCA is a critical artery which has an extensive clinical significance.
The orbital branches of the middle cerebral artery supply the inferior frontal gyrus as well as the lateral orbital surface of the frontal lobe. Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery MCA The middle cerebral artery arteria cerebri media is the largest of the carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain1. The inferior lower or infrasylvian MCA branch gives rise to arteries that supply the lateral temporal lobe including its anterior tip and the amygdala posterior parietal.
It branches off the internal carotid artery. The MCA arises from the internal carotid and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. The frontal branches supply the precentral middle and inferior frontal gyri.
Move the cursor along the course of the anterior and middle cerebral artery and its branches to identify individual segments and their perfusion targets. 8 rows In the 5th gestational week a plexiform vascular network originates near the anterior cerebral. The middle cerebral arteries supply the majority of the lateral surface of the hemisphere except the superior portion of the parietal lobe via the ACA and the inferior portion of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe via the PCA.
The middle cerebral artery MCA is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. A middle cerebral artery stroke occurs when the middle cerebral artery the largest branch of the internal carotid artery is blocked. The middle cerebral artery MCA is one of the three major paired arteries that supply blood to the cerebrumThe MCA arises from the internal carotid and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex.

Middle Cerebral Artery Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13734/middle-cerebral-artery_english.jpg)
Middle Cerebral Artery Anatomy Branches Supply Kenhub

Middle Cerebral Artery Wikipedia
Middle Cerebral Artery Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy

Middle Cerebral Artery Operative Neurosurgery
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/middle-cerebral-artery/Z3kPNo9AeYobOFFpQWPWQ_Ozcn2x81beEbLydTy6reIg_A._cerebri_media__01.png)
0 comments
Post a Comment